Pagination Query
Pagination
easy-query provides very simple pagination query functionality, making it convenient for users to perform paginated data queries.
Note!!!
pageIndexstarts from 1
Simple Pagination
EasyPageResult<Topic> topicPageResult = easyQuery
.queryable(Topic.class)
.where(o -> o.id().isNotNull())
.toPageResult(1, 20);
==> Preparing: SELECT COUNT(*) FROM t_topic t WHERE t.`id` IS NOT NULL
<== Total: 1
==> Preparing: SELECT t.`id`,t.`stars`,t.`title`,t.`create_time` FROM t_topic t WHERE t.`id` IS NOT NULL LIMIT 20
<== Total: 20Join Pagination
EasyPageResult<BlogEntity> page = easyQuery
.queryable(Topic.class)
.innerJoin(BlogEntity.class, (t, t1) -> t.id().eq(t1.id()))
.where((t, t1) -> {
t1.title().isNotNull();
t.id().eq("3");
})
.select(BlogEntity.class, (t, t1) -> Select.of(
t1.FETCHER.allFieldsExclude(t1.id())
))
.toPageResult(1, 20);
==> Preparing: SELECT COUNT(*) FROM t_topic t INNER JOIN t_blog t1 ON t.`id` = t1.`id` WHERE t1.`title` IS NOT NULL AND t.`id` = ?
==> Parameters: 3(String)
<== Total: 1, Query Use: 3(ms)
==> Preparing: SELECT t1.`create_time`,t1.`update_time`,t1.`create_by`,t1.`update_by`,t1.`deleted`,t1.`title`,t1.`content`,t1.`url`,t1.`star`,t1.`publish_time`,t1.`score`,t1.`status`,t1.`order`,t1.`is_top`,t1.`top` FROM t_topic t INNER JOIN t_blog t1 ON t.`id` = t1.`id` WHERE t1.`title` IS NOT NULL AND t.`id` = ? LIMIT 1
==> Parameters: 3(String)
<== Total: 1, Query Use: 2(ms)Group Pagination
EasyPageResult<BlogEntity> page = easyQuery
.queryable(Topic.class)
.innerJoin(BlogEntity.class, (t_topic, t_blog) -> t_topic.id().eq(t_blog.id()))
.where((t_topic, t_blog) -> t_blog.title().isNotNull())
.groupBy((t_topic, t_blog)-> GroupKeys.of(t_blog.id()))
.select(BlogEntity.class, group -> Select.of(
group.key1().as("id"),
//group.sum(t->t.t2.score()).as("score")//Both methods are the same, just difference between collection method and property method
group.groupTable().t2.score().sum().as("score")
))//t1.column(BlogEntity::getId).columnSum(BlogEntity::getScore)
.toPageResult(1, 20);
==> Preparing: SELECT COUNT(*) FROM (SELECT t1.`id`,SUM(t1.`score`) AS `score` FROM t_topic t INNER JOIN t_blog t1 ON t.`id` = t1.`id` WHERE t1.`title` IS NOT NULL GROUP BY t1.`id`) t2
<== Total: 1, Query Use: 8(ms)
==> Preparing: SELECT t1.`id`,SUM(t1.`score`) AS `score` FROM t_topic t INNER JOIN t_blog t1 ON t.`id` = t1.`id` WHERE t1.`title` IS NOT NULL GROUP BY t1.`id` LIMIT 20
<== Total: 20, Query Use: 2(ms)Custom Pagination Return Result
easy-query provides custom pagination return results, users can define pagination results themselves. See 《Replace Framework Behavior❗️❗️❗️》
Replace Interface
EasyPageResultProvider
| Method | Parameters | Description |
|---|---|---|
| createPageResult | long pageIndex, long pageSize,long total, List<T> data | Returns the pagination object for toPageResult |
| createShardingPageResult | long pageIndex, long pageSize,long total, List<T> data,SequenceCountLine sequenceCountLine | Returns the pagination object for toShardingPageResult |
Default Implementation
public class DefaultEasyPageResultProvider implements EasyPageResultProvider{
@Override
public <T> EasyPageResult<T> createPageResult(long pageIndex, long pageSize,long total, List<T> data) {
return new DefaultPageResult<>(total,data);
}
@Override
public <T> EasyPageResult<T> createShardingPageResult(long pageIndex, long pageSize,long total, List<T> data,SequenceCountLine sequenceCountLine) {
return new DefaultShardingPageResult<>(total,data,sequenceCountLine);
}
}
public class DefaultPageResult<T> implements EasyPageResult<T> {
private final long total;
private final List<T> data;
public DefaultPageResult(long total, List<T> data) {
this.total = total;
this.data = data;
}
public long getTotal() {
return total;
}
public List<T> getData() {
return data;
}
}
public interface EasyShardingPageResult<T> extends EasyPageResult<T>{
List<Long> getTotalLines();
}
public class DefaultShardingPageResult<T> implements EasyShardingPageResult<T> {
private final long total;
private final List<T> data;
private final SequenceCountLine sequenceCountLine;
public DefaultShardingPageResult(long total, List<T> data,SequenceCountLine sequenceCountLine) {
this.total = total;
this.data = data;
this.sequenceCountLine = sequenceCountLine;
}
public long getTotal() {
return total;
}
public List<T> getData() {
return data;
}
@Override
public List<Long> getTotalLines() {
return sequenceCountLine.getTotalLines();
}
}Implement Custom Pagination Return
For example, the default return for mybatis-plus is not data but records. How should eq return records?
public class MyPageResult<T> extends DefaultPageResult<T> {
public MyPageResult(long total, List<T> data) {
super(total, data);
}
//Override getData method, because jackson's default return doesn't care about fields, only getXXX methods
@JsonProperty("records")
@Override
public List<T> getData() {
return super.getData();
}
}To implement the EasyPageResultProvider interface, we just need to extend the default DefaultEasyPageResultProvider, no need to implement it from scratch:
public class MyEasyPageResultProvider extends DefaultEasyPageResultProvider {
@Override
public <T> EasyPageResult<T> createPageResult(long pageIndex, long pageSize, long total, List<T> data) {
return new MyPageResult<>(total,data);
}
}Finally, refer to the replace framework implementation documentation to replace the default implementation Click here
Use Your Own PageResult Without Dependency
Many times, the framework-provided EasyPageResult<T> provides convenience while making the entire project highly dependent on easy-query, which is not good. So easy-query provides custom PageResult<TResult> results in version 1.4.25 and provides chainable method calls for developer convenience.
Framework-Provided Paginator
Pager<TEntity,TPageResult> Users can implement pagination themselves
Add Your Own Pagination Return Result Interface
//Interface
public interface PageResult<T> {
/**
* Return total count
* @return
*/
long getTotalCount();
/**
* Result content
* @return
*/
List<T> getList();
}
//Implementation
public class MyPageResult<TEntity> implements PageResult<TEntity> {
private final long total;
private final List<TEntity> list;
public MyPageResult(long total, List<TEntity> list){
this.total = total;
this.list = list;
}
@Override
public long getTotalCount() {
return total;
}
@Override
public List<TEntity> getList() {
return list;
}
}Custom Pager
public class MyPager<TEntity> implements Pager<TEntity,PageResult<TEntity>> {
private final long pageIndex;
private final long pageSize;
private final long pageTotal;
public MyPager(long pageIndex, long pageSize){
this(pageIndex,pageSize,-1);
}
public MyPager(long pageIndex, long pageSize, long pageTotal){
this.pageIndex = pageIndex;
this.pageSize = pageSize;
this.pageTotal = pageTotal;
}
@Override
public PageResult<TEntity> toResult(Query<TEntity> query) {
EasyPageResult<TEntity> pageResult = query.toPageResult(pageIndex, pageSize,pageTotal);
return new MyPageResult<>(pageResult.getTotal(),pageResult.getData());
}
}Test Code
//Business code returns custom PageResult<TEntity>
PageResult<TopicGenericKey> pageResult = easyQuery
.queryable(TopicGenericKey.class)
.whereById("1")
.toPageResult(new MyPager<>(1, 2));
Assert.assertEquals(1,pageResult.getTotalCount());
Assert.assertEquals("1",pageResult.getList().get(0).getId());Implement MybatisPlus's SearchCount
Some users want eq to provide functionality similar to MybatisPlus's SearchCount, where a boolean value can set whether pagination needs to query count. Actually, users can pass their own total as the third parameter of toPageResult. When users pass in total, the framework uses the passed total without performing a count query on the expression. Just need frontend and backend cooperation: after giving the first total to the user, keep interacting with it afterward.
Of course, some users want to control it through a boolean value, so how should we implement it? Please see the case below.
Implement Pager
The second generic of Pager can use the framework's or define it yourself:
public class SearchCountPager<TEntity> implements Pager<TEntity, PageResult<TEntity>> {
private final long pageIndex;
private final long pageSize;
private final boolean searchCount;
public SearchCountPager(long pageIndex, long pageSize, boolean searchCount) {
this.pageIndex = pageIndex;
this.pageSize = pageSize;
this.searchCount = searchCount;
}
@Override
public PageResult<TEntity> toResult(PageAble<TEntity> query) {
if (searchCount) {
EasyPageResult<TEntity> pageResult = query.toPageResult(pageIndex, pageSize);
return new MyPageResult<>(pageResult.getTotal(), pageResult.getData());
}
//Set how many items to get each time
long take = pageSize <= 0 ? 0 : pageSize;
//Set current page number minimum 1
long index = pageIndex <= 0 ? 1 : pageIndex;
//How many items to skip
long offset = (index - 1) * take;
List<TEntity> list = ((Query<TEntity>) query).limit(offset, take).toList();
return new MyPageResult<>(-1, list);
}
public static <TEntity> SearchCountPager<TEntity> of(long pageIndex, long pageSize, boolean search){
return new SearchCountPager<>(pageIndex,pageSize,search);
}
}Query Count
PageResult<Topic> pageResult = easyEntityQuery.queryable(Topic.class)
.where(t_topic -> {
t_topic.title().like("123");
}).toPageResult(SearchCountPager.of(1, 10, true));
==> Preparing: SELECT COUNT(*) FROM `t_topic` WHERE `title` LIKE ?
==> Parameters: %123%(String)
<== Time Elapsed: 3(ms)
<== Total: 1
==> Preparing: SELECT `id`,`stars`,`title`,`create_time` FROM `t_topic` WHERE `title` LIKE ? LIMIT 10
==> Parameters: %123%(String)
<== Time Elapsed: 2(ms)
<== Total: 10Don't Query Count
PageResult<Topic> pageResult = easyEntityQuery.queryable(Topic.class)
.where(t_topic -> {
t_topic.title().like("123");
}).toPageResult(SearchCountPager.of(1, 10, false));
==> Preparing: SELECT `id`,`stars`,`title`,`create_time` FROM `t_topic` WHERE `title` LIKE ? LIMIT 10
==> Parameters: %123%(String)
<== Time Elapsed: 2(ms)
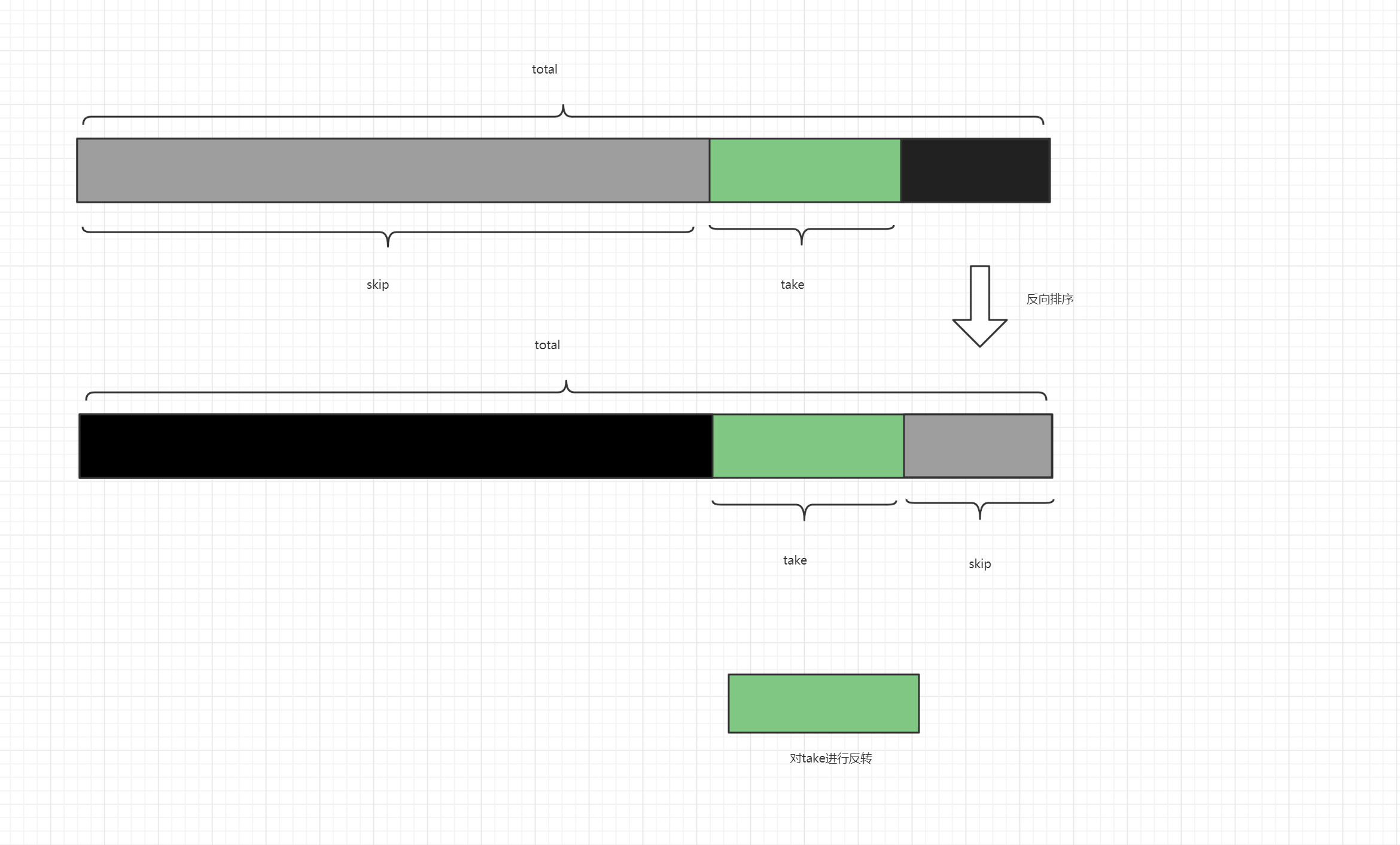
<== Total: 10Reverse Sort Pagination
When we use pagination queries
The specific principle is shown in the following diagram:
Configuration
| Configuration Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| reverseOffsetThreshold | 0 | Reverse sort offset threshold. For example, if set to 10000, then during pagination if offset > the set value 10000 AND offset > (total*0.5), meaning the query offset exceeds half of the total, reverse sorting will be enabled |
Enable programmatically:
easyQueryClient = EasyQueryBootstrapper.defaultBuilderConfiguration()
.setDefaultDataSource(dataSource)
.optionConfigure(op -> {
op.setReverseOffsetThreshold(10);
})
.useDatabaseConfigure(new MySQLDatabaseConfiguration())
.build();Example
From the example we can see that when our offset is greater than half of the total and greater than the reverse sort threshold 10, then asc becomes desc, and deep pagination becomes shallow pagination:
EasyPageResult<Topic> pageResult = easyEntityQuery.queryable(Topic.class)
.where(t_topic -> {
t_topic.id().isNotNull();
}).orderBy(t_topic -> t_topic.createTime().asc()).toPageResult(7, 10);
==> Preparing: SELECT COUNT(*) FROM `t_topic` WHERE `id` IS NOT NULL
<== Time Elapsed: 3(ms)
<== Total: 1
==> Preparing: SELECT `id`,`stars`,`title`,`create_time` FROM `t_topic` WHERE `id` IS NOT NULL ORDER BY `create_time` DESC LIMIT 10 OFFSET 31
<== Time Elapsed: 3(ms)
<== Total: 10Don't Enable Reverse Sort at Runtime
EasyPageResult<Topic> pageResult = easyEntityQuery.queryable(Topic.class)
.configure(op->{
//Set not to use reverse sort pagination
op.setReverseOrder(false);
})
.where(t_topic -> {
t_topic.id().isNotNull();
}).orderBy(t_topic -> t_topic.createTime().asc())
.toPageResult(7, 10);
==> Preparing: SELECT COUNT(*) FROM `t_topic` WHERE `id` IS NOT NULL
<== Time Elapsed: 2(ms)
<== Total: 1
==> Preparing: SELECT `id`,`stars`,`title`,`create_time` FROM `t_topic` WHERE `id` IS NOT NULL ORDER BY `create_time` ASC LIMIT 10 OFFSET 60
<== Time Elapsed: 3(ms)
<== Total: 10